Vascular Surgery
Vascular Surgery
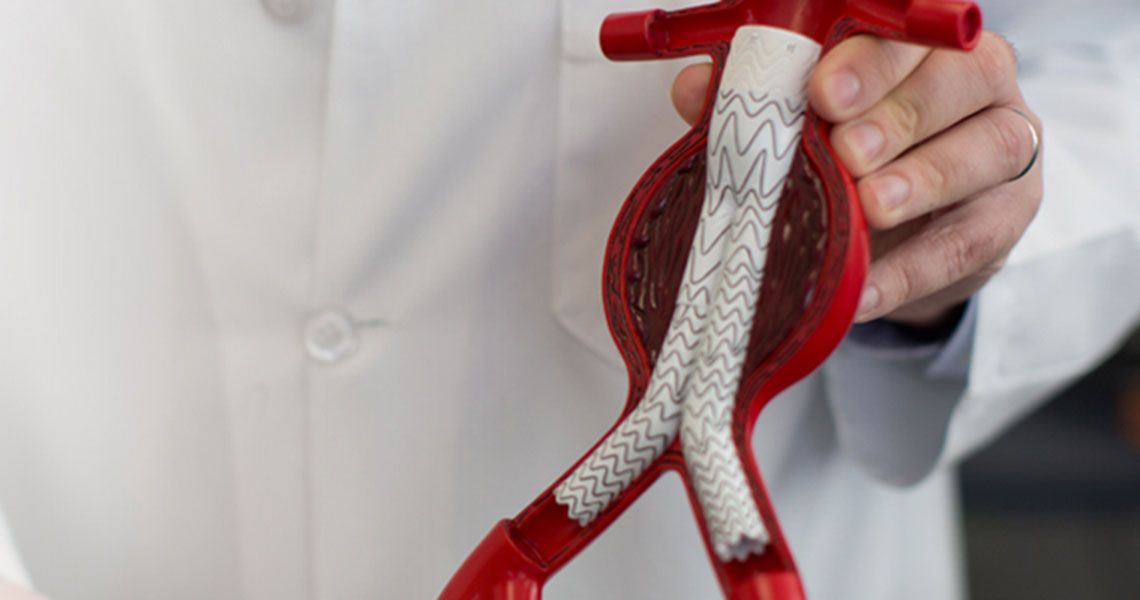
Services We Offer & Conditions We Treat:
- We diagnose and treat:
-
- Thoracic aortic dissection and aneurysms
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms
- Carotid artery disease
- Peripheral artery disease
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Mesenteric and renal artery disease
- Dialysis access/AV fistula
- Venous insufficiency
- Varicose veins
- Venous ulcers
- Your physician may utilize:
-
- Ultrasound technology to screen aortic aneurysms, diagnose carotid stenosis to prevent stroke, and detect decreased blood flow to the legs to prevent amputation.
- Advanced endovascular technology such as laser atherectomy and shock-wave therapy to treat arterial occlusive disease of the leg arteries in a minimally invasive fashion.
- Surgical bypass to treat peripheral vascular disease for limb salvage
- Both standard and complex fenestrated stent grafts as well as open resection to treat aortic aneurysms of the entire aorta, from the aortic arch to the abdominal aorta.
- Transfemoral and trans-carotid (TCAR) stenting techniques as well as carotid endarterectomy with EEG monitoring to treat carotid stenosis to prevent strokes
- Endovascular and open techniques to create and revise dialysis access such as AV fistulas and AV grafts
- Minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty, stenting, and atherectomy — all designed to restore blood flow safely and quickly.
- Specific methods of treatment:
-
- Bypass surgery
- Endartectomy
- Angioplasty
- Endovascular aneurysm repair
- Endovascular therapy
- Endovenous ablation
- Open aneurysm repair
- Stent
- Surgical vein stripping
- Thoracic Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (TEVAR)
- Thrombolytic therapy
Treatment for Vascular Disorders
Learn More about our dedicated Non-Invasive Vascular Laboratory
At the George Washington Medical Faculty Associates, our vascular surgeons are highly experienced in the evaluation, prevention, and treatment of all vascular disorders. Using state-of-the-art technology, we offer a full spectrum of treatment options, including minimally invasive options for patients with vascular conditions that range from simple varicose veins to complex aortic diseases, and everything in between.
George Washington University has a long tradition of excellence in patient care, innovative methods, education and training, and clinical and basic science research in vascular diseases. We specialize in peripheral vascular disease, aneurysms, aortic dissection and carotid artery disease. Our commitment to patients is singular and we commit to provide first-class care to our patients by utilizing the most effective, cutting-edge techniques to treat vascular diseases.
As a patient, or as a physician referring a patient, you have the convenience of having specialists from several disciplines all in one location. Whether it is inpatient or outpatient services, advanced preventative care or participating in clinical trials, The GW Medical Faculty Associates Vascular Diseases Program offers it all. Our surgeons are highly skilled in both endovascular and open surgery techniques to provide the patients with an individualized plan of care that suits the unique anatomy and clinical condition of each patient. At George Washington University, our surgeons enlist the patients and their families as our partners to collaborate and make informed decisions with all treatment team members. We provide support with all available resources to make follow-up care as smooth and convenient as possible for our patients.
- Vascular Disease Overview
-
Vascular disease refers to an abnormality of the blood vessels (veins or arteries). Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) refers to abnormality of blood vessels throughout the body except those in the heart and brain. Arteries carry blood from the heart to other parts of the body. Veins carry blood to the heart from the legs and other organs in the body. Vascular disease results from degeneration of normal arteries and veins as the result of the normal aging process and can be made worse by certain factors that damage blood vessels. Treatments aimed at reducing vascular damage can slow down and sometimes reverse vascular disease, or give the body a chance to “heal itself.” When these kinds of efforts are not sufficient, surgery may be required to correct abnormalities.
- Arterial Conditions
-
The arteries and veins transport blood throughout the body. When these pathways are affected by a disease or abnormality, the heart and other parts of the body cannot function properly which could result in life-threatening events like a heart attack or stroke. In the early stages, these conditions can usually be treated through lifestyle changes and medications. If the condition has progressed a significant amount that it presents an immediate danger to the patient, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Arterial conditions we treat include:
- Atherosclerosis– Cholesterol and calcium build up in the arteries and create a substance called artery plaque. When artery plaque becomes severe, it narrows the arteries and increases the risk of blood clot, heart attack, and stroke.
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)– This is a type of atherosclerosis that impedes blood flow to the legs and/or arms. It is a very common condition that typically occurs in patients 60 and older.
- Carotid Artery Disease – The carotid arteries supply blood to the brain. Atherosclerosis in these veins is very serious as it significantly increases the risk of stroke. There are several surgeries that can treat this condition if it presents an immediate danger to the patient.
- Aneurysm – An aneurysm is a bulging in the blood vessel caused by damage to the vessel wall. Aneurysms that are left untreated can rupture and cause serious damage to the heart and other parts of the body.
At GW Medical Faculty Associates, our vascular surgeons can intervene before these conditions result in life-threatening events. Be sure to discuss cardiovascular health with your primary care physician to assess your risk for any of these conditions.
- Vascular Lab
-
GW Medical Faculty Associates Dedicated Non-Invasive Vascular Laboratory
The Non-Invasive Vascular Laboratory is the backbone of a successful Vascular Surgery practice This discipline utilizes high frequency soundwaves and segmental blood pressures to evaluate how blood travels through arteries and veins The most common exams offered evaluates patients for Stroke, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA), Peripheral Arterial Disease of the legs (PAD) and Varicose Veins
Where are you located?We are located at 2150 Pennsylvania Avenue NW Washington DC 20037 in the Department of Surgery, Division of Vascular Surgery at GW Medical Faculty Associates on the 6th floor south.
What are your hours of operation?
Monday thru Friday 8am to 4:30pmHow do we contact your department?
Main Number: 202-741-2494
Dr. Bao-Ngoc Nguyen, Medical Director
Mark Bates, RVT, Technical DirectorWhat is a Dedicated Non Invasive Vascular Laboratory?
A specialized diagnostic testing facility that is staffed by Registered Vascular Technologists (RVT®), who use a variety of medical devices that produce soundwaves to evaluate blood vessels and organs within the body. The term “Non Invasive” means that this technology acquires its data with devices that are used outside of the body and does not require needlesticks or catheters.What are the most frequently ordered exams?
- Carotid Duplex Imaging
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the great blood vessels within the neck that directly sends blood to the brain. The most common request for this study is to evaluate the patient for concerns of BRAIN ATTACK (STROKE).
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the great blood vessels within the neck that directly sends blood to the brain. The most common request for this study is to evaluate the patient for concerns of BRAIN ATTACK (STROKE).
- Aorta Duplex Imaging
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the great blood vessel within the abdomen that sends blood to multiple organs and to the pelvis and legs. The most common request for this study is to evaluate for a weakening or bulging (ANEURYSM) or plaque within the vessel that causes a reduction in blood flow to the organs (ATHEROSCLEROSIS).
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the great blood vessel within the abdomen that sends blood to multiple organs and to the pelvis and legs. The most common request for this study is to evaluate for a weakening or bulging (ANEURYSM) or plaque within the vessel that causes a reduction in blood flow to the organs (ATHEROSCLEROSIS).
- Peripheral Artery Doppler
- Utilizing a small “pencil shaped” probe and blood pressure cuffs to evaluate blood flow in blood vessels of the arms and legs. The most common request for this study is to evaluate the extremities for pain and tiredness in the muscles with motion or most commonly referred to as PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE (PAD).
- Utilizing a small “pencil shaped” probe and blood pressure cuffs to evaluate blood flow in blood vessels of the arms and legs. The most common request for this study is to evaluate the extremities for pain and tiredness in the muscles with motion or most commonly referred to as PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE (PAD).
- Venous Duplex Imaging
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the venous blood vessels of the arms and legs. The most common request for this study is for pain and swelling or BLOOD CLOT (DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS OR DVT).
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the venous blood vessels of the arms and legs. The most common request for this study is for pain and swelling or BLOOD CLOT (DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS OR DVT).
- Venous Duplex Imaging for Reflux/Insufficiency
- Utilizing ultrasound and Doppler to evaluate the small valves within the veins that control blood flow direction and pressure. The most common request for this study is to evaluate the legs for bulging veins that contribute to leg heaviness, fatigue and ankle and foot swelling (VARICOSE VEINS).
- Carotid Duplex Imaging
- Venous Conditions
Although peripheral vascular disease can often be treated with lifestyle changes and risk factor management, medications (such as sclerosing agents or blood thinners), catheter-based treatments or open surgery may be required.


